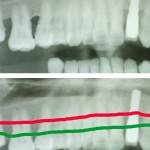
Wouldn’t you like to know whether your dentist is good or bad?
We assume you do, which is why this week we are going to tell you all about what to consider when looking for a dentist and how to find a good one.
As usual, we will provide you with an overview of this week’s main topic!
- Good dentist – the cost estimate
- Dentists and their teams
- Hygiene in the dentist’s office
- Explaining procedures
- Trouble-shooting
Good dentist – the cost estimate
 First of all, does your dentist even bother giving you a cost estimate?
First of all, does your dentist even bother giving you a cost estimate?
No? Then s/he has no idea what s/he is doing!
If yes, how is the estimate structures?
Did you get a thorough check-up before you got the estimate? You should know what has to be done in your case and what will only be performed to fill the dentist’s pockets. What are we going on about? Well, in order for the dentist to provide you with a good cost estimate, s/he needs to have a good idea of the current status of your teeth and mouth.
If s/he does not bother performing a check-up, then it is likely s/he will only do things that cost a lot, namely implants and crowns.
You can always tell good estimates from bad ones, because good estimates always provide detailed information, which is collected during a check-up (assuming, of course, that your mouth really needs an overhaul, not just one bridge or implant if your teeth and mouth are otherwise healthy, otherwise, what would be the point of collecting data!).
A good cost estimate includes:
- An anamnesis (medical history) / Patient’s request
- Findings
- Diagnosis
- Recommendations for therapy / Alternatives
- Description of procedures as needed
This information lets the dentist know what you wish to be done, the condition of your teeth (periodontal status, photos, models of your teeth, …), anything and everything you’ll need to set up a treatment plan.
–
The cost estimate should consider all kinds of work, even work which is less lucrative to the dentist. This includes fillings, root canal treatment, operations such as removing wisdom teeth, etc.
–
But this is the kind of work which should usually be done first, before doing more complicated procedures – you should make sure the ground is in good shape before you start building houses on it (crowns, implants etc.).
–
Summing up, a simple cost estimate can and should tell you quite a lot!
- If your dentist offers you any treatment without performing a thorough check-up first, then chances are that s/he is only going to do things which cost the most money!
- If the cost estimate starts out with an extensive check-up, then you’re on the right path!
- If a cost estimate begins with the least expensive types of treatment (renewed root treatment, removing wisdom teeth, periodontal work, …) with dentures (crowns, bridges) last on the list, then stick with that dentist!
More on this topic tomorrow, and by the end of the week you should be able to tell a good dentist from all others!
VN:F [1.9.22_1171]
Rating: 0.0/5 (0 votes cast)
VN:F [1.9.22_1171]