How long should you bother keeping a tooth?
Get a tooth removed, or wait, but for how long? As long as you still have good reason to!
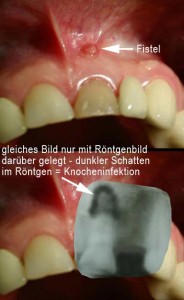
 We are talking about severely damaged teeth, teeth that have undergone root treatment but are still causing problems. The picture shows you a tooth that there is no more reason to keep.
We are talking about severely damaged teeth, teeth that have undergone root treatment but are still causing problems. The picture shows you a tooth that there is no more reason to keep.
The patient underwent root treatment 4 years previously and is still experiencing pain in this area. Root tip resection was performed, but to no avail. During the root tip resection, the tooth received neither an orthograde nor a retrograde filling – more on this topic here
–
The patient opted for another resection, but in the course of the operation it became evident that the tooth needed extraction.
–
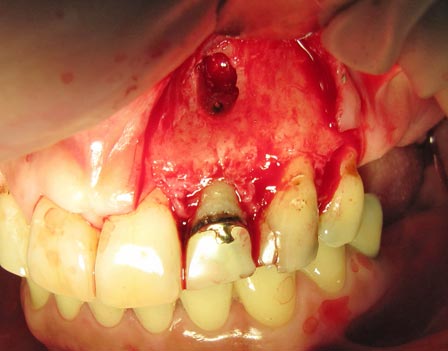
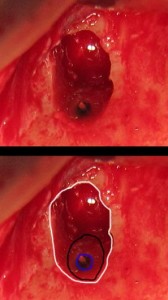 The mucous membrane has been flipped to the side, you can see a small window of bone (highlighted in white), and you can clearly see the tooth (highlighted in black) – the root tip has already been cut. The inside of the tooth is highlighted in blue, inside the pink dot you can see the filling compound. Around the compound, however, the tooth has started to rot – the black area. There is no more point in keeping this tooth, as faulty root treatment has caused the tooth to rot from the inside. Another root tip resection may help to put off the problem for a while, but not eliminate it completely!
The mucous membrane has been flipped to the side, you can see a small window of bone (highlighted in white), and you can clearly see the tooth (highlighted in black) – the root tip has already been cut. The inside of the tooth is highlighted in blue, inside the pink dot you can see the filling compound. Around the compound, however, the tooth has started to rot – the black area. There is no more point in keeping this tooth, as faulty root treatment has caused the tooth to rot from the inside. Another root tip resection may help to put off the problem for a while, but not eliminate it completely!